The Ultimate Guide To Companion Planting
The Ultimate Guide to Companion Planting
Companion planting is a gardening technique that involves planting certain plants together to benefit each other. This can be done to attract beneficial insects, repel pests, improve soil quality, or increase yields.
There are many different companion planting combinations that can be used, and the best ones for your garden will depend on the specific plants you are growing. However, there are some general principles that can help you get started.
Benefits of Companion Planting
There are many benefits to companion planting, including:
- Increased yields: Companion planting can help to increase yields by attracting beneficial insects, which help to pollinate plants and control pests.
- Improved soil quality: Companion plants can help to improve soil quality by fixing nitrogen, breaking down organic matter, and attracting earthworms.
- Reduced pest problems: Companion plants can help to repel pests, such as aphids, beetles, and rabbits.
- Attracted beneficial insects: Companion plants can attract beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and spiders, which help to control pests.
- Enhanced flavor: Some companion plants can enhance the flavor of other plants. For example, mint planted near tomatoes can help to improve the flavor of the tomatoes.
How to Choose Companion Plants
When choosing companion plants, there are a few things to keep in mind:
- Plants with similar needs: Companion plants should have similar needs for sunlight, water, and soil type. This will help to ensure that they will both thrive in the same environment.
- Attract beneficial insects: Some plants attract beneficial insects, which can help to control pests. For example, marigolds attract ladybugs, which eat aphids.
- Repels pests: Some plants repel pests. For example, mint repels mosquitoes and ants.
- Improve soil quality: Some plants improve soil quality by fixing nitrogen, breaking down organic matter, or attracting earthworms. For example, beans fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Enhance flavor: Some companion plants enhance the flavor of other plants. For example, mint planted near tomatoes can help to improve the flavor of the tomatoes.
Common Companion Planting Combinations
Here are some common companion planting combinations:
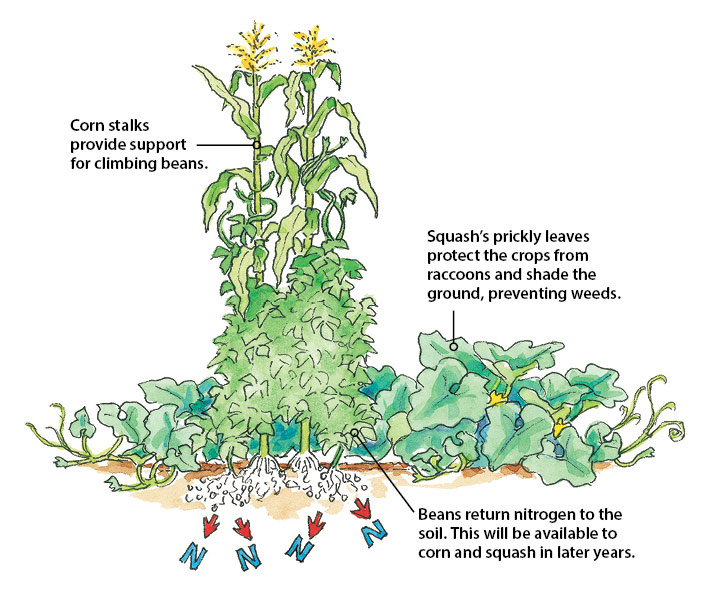
- Beans and corn: Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits the corn. Corn provides shade for the beans, which helps to prevent them from getting too hot.
- Carrots and onions: Onions repel carrot flies, which can damage carrots. Carrots help to improve the flavor of onions.
- Garlic and tomatoes: Garlic repels tomato hornworms, which can damage tomatoes. Tomatoes provide shade for the garlic, which helps to prevent it from getting too hot.
- Lettuce and chives: Chives repel aphids, which can damage lettuce. Lettuce provides shade for the chives, which helps to prevent them from getting too hot.
- Marigolds and tomatoes: Marigolds attract ladybugs, which eat aphids. Tomatoes provide shade for the marigolds, which helps to prevent them from getting too hot.
Conclusion
Companion planting is a great way to improve your garden's health and productivity. By choosing the right companion plants, you can attract beneficial insects, repel pests, improve soil quality, and increase yields.
If you are new to companion planting, start by experimenting with a few different combinations. You will soon find that companion planting is a fun and rewarding way to grow a healthy and productive garden.
Companion planting is a gardening technique that involves planting certain plants together to benefit each other. Some plants can help to attract beneficial insects, while others can help to repel pests. By planting the right plants together, you can help to improve your garden's health and productivity.
If you're interested in learning more about companion planting, I recommend visiting Gardenia Inspiration. This website has a comprehensive guide to companion planting, including a list of good companion plants for a variety of vegetables.
In addition to the information on the website, you can also find helpful tips and advice on companion planting by talking to other gardeners. There are many gardening forums and blogs where you can ask questions and get advice from experienced gardeners.
FAQ of good companion plants
Q: What are companion plants?
A: Companion plants are two or more different types of plants that are planted together because they benefit each other in some way. For example, some companion plants attract beneficial insects that help to control pests, while others improve the soil quality or deter pests.
Q: How do I choose good companion plants?
A: There are a few things to consider when choosing good companion plants. First, you need to think about the type of plants you want to grow. Some companion plants are only beneficial for certain types of plants, so it's important to match them up correctly. Second, you need to consider the climate and soil conditions in your area. Some companion plants prefer different conditions, so you need to make sure they'll be happy in your garden. Finally, you need to consider your own personal preferences. Some people prefer to plant companion plants that have complementary colors or scents.
Q: What are some examples of good companion plants?
A: There are many different examples of good companion plants, but here are a few popular ones:
- Tomatoes and basil: Basil repels certain insect pests that can damage tomatoes, such as thrips and whiteflies.
- Peas and beans: Peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits beans. Beans also help to suppress weeds.
- Carrots and onions: Onions repel carrot fly, a common pest of carrots.
- Cabbage and nasturtiums: Nasturtiums attract beneficial insects that help to control pests that damage cabbage.
- Squash and melons: Marigolds repel cucumber beetles, a common pest of squash and melons.
Q: What are some benefits of companion planting?
A: There are many benefits to companion planting, including:
- Increased crop yields
- Improved plant health
- Reduced pest and disease problems
- Increased biodiversity
- Enhanced soil quality
Q: How do I plant companion plants?
A: There are a few different ways to plant companion plants. You can plant them together in the same bed, or you can plant them in different beds but close enough together that they can benefit each other. When planting companion plants, it's important to follow the specific instructions for each type of plant.
Image of good companion plants
- Tomatoes and Basil: Basil repels certain insect pests such as thrips and also disorientates moths which lay tomato hornworms.
- Carrots and Parsley: Carrots and parsley help each other grow by attracting different insects. Carrots attract carrot flies, while parsley attracts hoverflies, which prey on carrot flies.

- Cucumbers and Marigolds: Marigolds repel cucumber beetles, which can be a major pest of cucumbers.
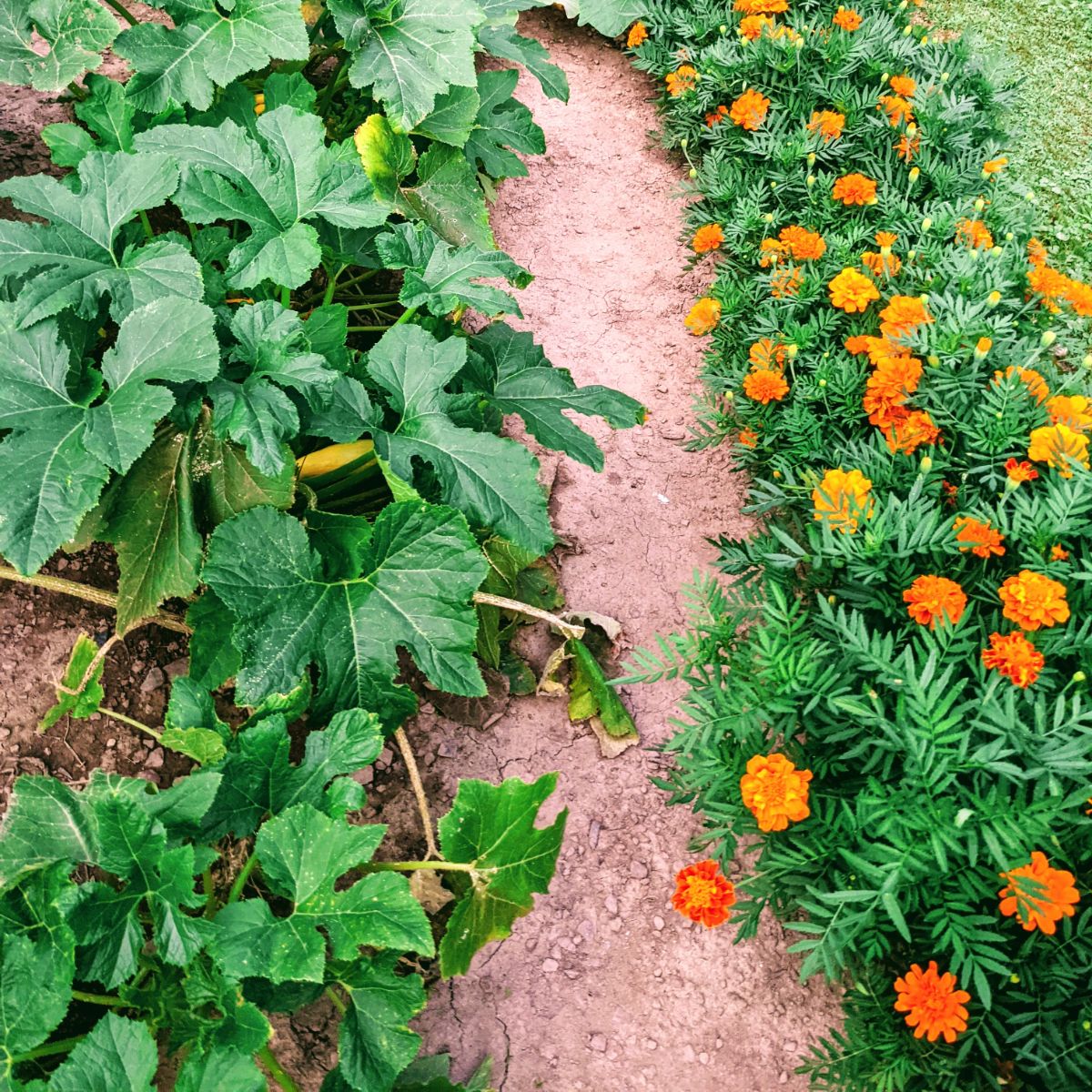

- Beans and Peas: Beans and peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits other plants. They also help each other by providing support for each other.
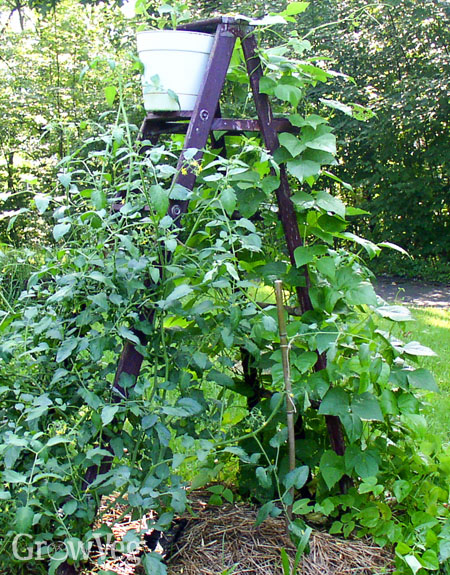

- Squash, Beans, and Corn: This trio is known as the "Three Sisters" and has been planted together by Native Americans for centuries. The beans provide nitrogen for the corn, the corn provides support for the beans, and the squash shades the soil, which helps to keep it moist.
Post a Comment for "The Ultimate Guide To Companion Planting"